
The researchers found that "effective screening depends largely on frequency of testing and speed of reporting and is only marginally improved by high test sensitivity." Humanitarian uses Larremore et al simulated various COVID-19 population screening strategies. Mina et al theorized that higher-frequency screening using lower-sensitivity RATs may be more useful than lower-frequency screening using higher-sensitivity PCR tests because the former would "capture most infections while they are still infectious." The quick results of RATs would serve to limit asymptomatic spread. Screening all students every two days with a "low-sensitivity, high-specificity test" (such as a RAT) would be able to control an outbreak of COVID-19. Paltiel et al studied a hypothetical college campus with 5000 students. Second, the person with a positive Antigen-RDT could be asymptomatic but a "contact of a probable or confirmed case." Nevertheless, individual countries may have different case definitions of COVID-19 for example, in New Zealand a positive PCR test (not just a RAT) is necessary for a person to be considered a "confirmed case." Use in screening īetween mid-2020 and early 2021, studies using mathematical models estimated the benefit of frequent RATs in screening populations for COVID-19. First, the person with a positive Antigen-RDT could meet a "probable case definition" such as having recent loss of smell or taste without any known cause, or could meet certain "suspect criteria" such as having a severe acute respiratory illness. The World Health Organization (WHO) COVID-19 Case Definition states that a person with a positive RAT (also known as an antigen rapid diagnostic test or Antigen-RDT) can be considered a "confirmed case of SARS-CoV-2 infection" in two ways. Uses Use in diagnosis ĬOVID-19 rapid antigen tests (RATs) have been widely used for diagnosis of COVID-19. The tests are more sensitive in the symptomatic and transmissive stages of disease when the viral load is higher. Despite this, COVID-19 RATs remain valuable in finding people who would otherwise not know they were infected, helping to prevent further transmission. However, the tests have a sensitivity of 70%-72%, which is lower than COVID-19 polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests' sensitivity of 88%-96%. įalse positives are very rare the tests' specificity is 98%-99%. Many RATs can be used for self-testing, in which an individual "collects their own specimen… and interpret their test result themselves". RATs have been used in several countries as part of mass testing or population-wide screening approaches. They are quick to implement with minimal training, cost a fraction of other forms of COVID-19 testing, and give users a result within 5–30 minutes. To diagnose SARS-CoV-2 infections ( COVID-19)ĬOVID-19 rapid antigen tests or RATs, also frequently called COVID-19 lateral flow tests or LFTs, are rapid antigen tests used to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection ( COVID-19). SARS-CoV-2 or COVID-19 antigen test, rapid antigen detection test (RADT), lateral flow test (LFT), lateral flow device (LFD), antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic test (Ag-RDT), antigen rapid diagnostic test (Antigen-RDT), point of care (POC) test, rapid test

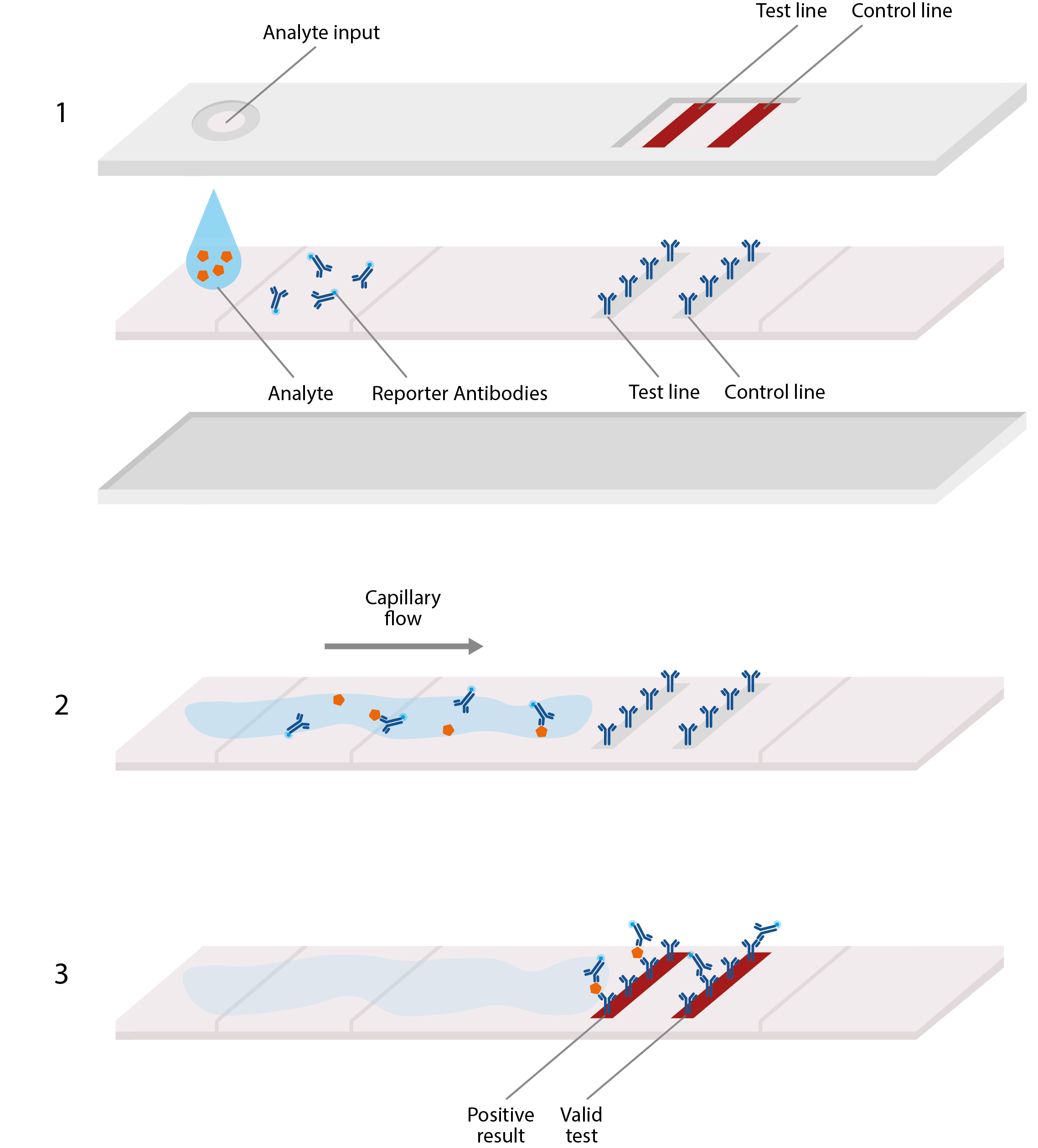
Negative (left, showing Control line) and positive (right, showing Control and Test lines) results


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
